Mathematics
In 1837, Charles Babbage invented The Analytical Engine, a
mechanical card-programmed digital computer which anticipated almost
every aspect of the electronic computers which would not appear for
more than a century afterward. These pages are a virtual museum where you can
explore the Engine both through historical documents and an
emulator which allows you to experience for yourself what it
would have been like to program a steam-powered computer.
New: 2017 update adds a JavaScript/HTML5 Web-based emulator and
several new sample programs.
Cellular Automata Laboratory
invites you to explore the world of cellular automata with
the aid of a high-speed programmable simulator which runs
within your Web browser. Cellular automata rules are defined
by short programs written in JavaScript or Java. Rule
definitions in JavaScript are compiled directly inside the
browser and do not require installing a programming
environment on your machine. The accompanying on-line
laboratory manual
explains the theory of cellular automata, how to use the simulator
programs, documents the many ready-to-run rules included,
describes how to create your own original experiments,
and contains a comprehensive bibliography. A development
kit supplies source code for all of the rule definitions
and the files they use, providing a starting point for your
own explorations. New:
2017 update
includes browser-based simulation and JavaScript rule
definition.
Five.
A neural network simulator associative
memory demonstration for the Commodore 64—really!
Includes complete source code in BASIC.
An informal introduction to analysis of experiments to determine
whether results are significant or consistent with chance.
Independent binary processes such as coin flipping and the output of
hardware random bit sequence generators are the focus of the
discussion.
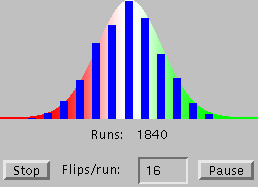 The
Probability Pipe
Organ lets you run interactive experiments which demonstrate how
the results from random data approach the normal
distribution expectation as the number of experiments grows large.
Update: HTML5 animation eliminates the need for Java applet
support. (The Java version
remains available.)
The
Probability Pipe
Organ lets you run interactive experiments which demonstrate how
the results from random data approach the normal
distribution expectation as the number of experiments grows large.
Update: HTML5 animation eliminates the need for Java applet
support. (The Java version
remains available.)
A program for the analysis (not generation) of random and
pseudorandom sequences. A variety of tests, including many from
Knuth, are applied to the contents of a file and the results reported
on standard output. In portable C; public domain. October 1998
update adds frequency histogram display, optional analysis of input as
a bitstream, CSV output for postprocessing by other programs, and
improved HTML documentation.
The travelling salesman problem—finding the shortest
itinerary to visit a set of cities— is a classic of
combinatorial optimisation: easy to state but hellishly
difficult to solve. This page demonstrates the technique of
simulated annealing to find near-optimal solutions to this
problem.
Before computers and calculators, there were slide rules. It is difficult for people today to appreciate just how magic it was to be
able to carry a small tool, made of bamboo and plastic, that could perform many of the computations of engineering and science which
used to be so tedious in mere seconds, as long as you were happy with its limited precision.
This document explores this vintage computing tool, using it to solve a variety of
problems ranging from loading a turnip truck to interstellar flight.
A simple mathematical game reminiscent of blackjack invites
you to flex both your intuitive and formal analytical
skills, while demonstrating how superficially unrelated topics
in mathematics may be deeply connected when examined in
more detail.
What can you learn, in three years of computer time, about
an obscure problem in recreational mathematics? Not very
much, at least in this case. But hey, negative results
are still results, right? And still the Quest beckons to
your idle loop. In 1995, Tim
Irvin continued the Quest to two million digits.
His story
illustrates both how fast computers have gotten in the the last five years,
and how much of that power is often devoted to the idle loop.
Units Calculator is a Web interface to the
GNU
Units utility which allows conversion among thousands of
physical units, constants, and currencies. Units Calculator
may be used to perform complex scientific and engineering
calculations involving physical units and guards against
common errors due to dimensional incompatibility. Units
Calculator is 100% compatible with GNU Units, but as a Web
application can be used from any platform with a Web browser.
Currency exchange rates and precious metal prices are updated
daily. See the Introduction
for a tutorial, or proceed directly to the
Expert page, which contains
a click-to-copy table of common units.
 The
Probability Pipe
Organ lets you run interactive experiments which demonstrate how
the results from random data approach the normal
distribution expectation as the number of experiments grows large.
Update: HTML5 animation eliminates the need for Java applet
support. (The Java version
remains available.)
The
Probability Pipe
Organ lets you run interactive experiments which demonstrate how
the results from random data approach the normal
distribution expectation as the number of experiments grows large.
Update: HTML5 animation eliminates the need for Java applet
support. (The Java version
remains available.)